Reverse lookup dns zone
Reverse lookup dns zones are used to provide address-to-name resolution. In this, A DNS client uses a known IP address and looks for the host name of that address.
The following illustrates the general reverse dns look up query process:
1. Assume IP address for which name resolution needed is 192.168.1.5.
2. A DNS client queries the DNS server for a pointer (PTR) resource record which maps the IP address 192.168.1.5 to a host name "user".
3.The DNS server reverses the address and appends the domain name "in-addr.arpa" to the end of the reversed IP address. Now the resultant address to search becomes "5.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. Now this fully qualified domain name (FQDN). i.e 5.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa be searched in a reverse lookup zone.
4. After the 5.1.168.192.in.addr.arpa is located in authoritative DNS server, the authoritative DNS server for 5.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa can respond with the pointer (PTR) resource record information which includes the DNS name "user.myrootdns.com" for the IP address 192.168.1.5, which completes the reverse lookup process.
To create reverse lookup zone, follow the link Create Reverse Lookup zone
The following illustrates the general reverse dns look up query process:
1. Assume IP address for which name resolution needed is 192.168.1.5.
2. A DNS client queries the DNS server for a pointer (PTR) resource record which maps the IP address 192.168.1.5 to a host name "user".
3.The DNS server reverses the address and appends the domain name "in-addr.arpa" to the end of the reversed IP address. Now the resultant address to search becomes "5.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. Now this fully qualified domain name (FQDN). i.e 5.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa be searched in a reverse lookup zone.
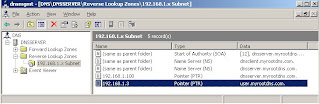 |
4. After the 5.1.168.192.in.addr.arpa is located in authoritative DNS server, the authoritative DNS server for 5.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa can respond with the pointer (PTR) resource record information which includes the DNS name "user.myrootdns.com" for the IP address 192.168.1.5, which completes the reverse lookup process.
To create reverse lookup zone, follow the link Create Reverse Lookup zone
0 comments:
Post a Comment